
- #Local by flywheel vs xampp how to#
- #Local by flywheel vs xampp install#
- #Local by flywheel vs xampp update#
- #Local by flywheel vs xampp full#
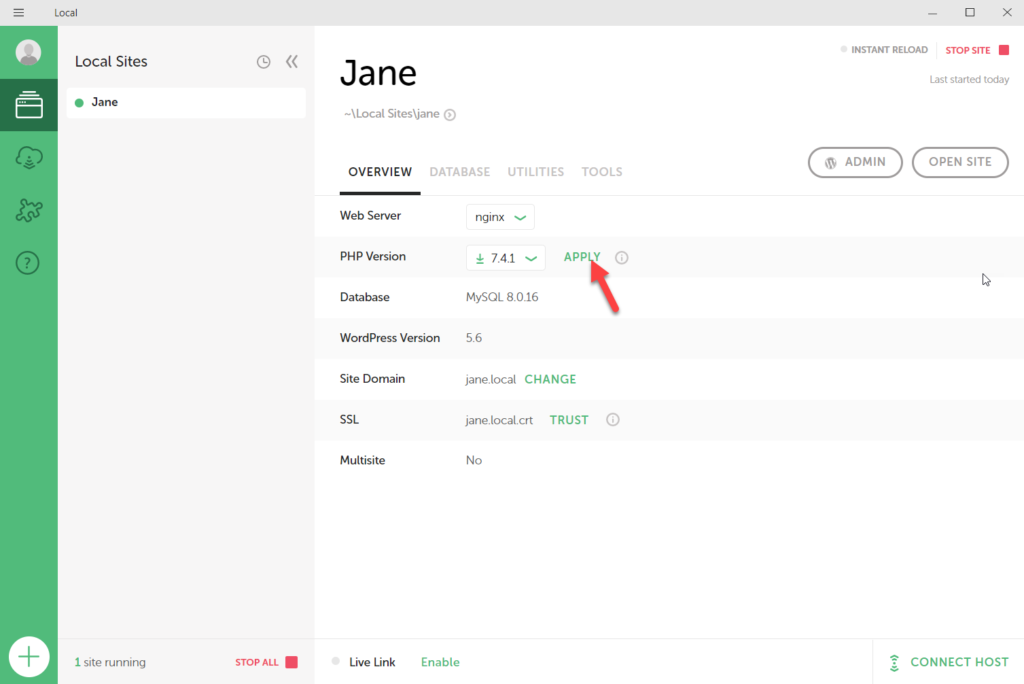
Here’s a quick example of a WordPress installation command in WP-CLI: $ wp core install -url=v -title="Local Website" -admin_user=johndoe -admin_password=wpcli You can even configure the installation using parameters, so you never need to open a browser window until WordPress is ready to go. The beauty of using WP-CLI is that you can download and install WordPress with only a few commands. However, you can also use WP-CLI locally to help you create websites: This setup lets you manage your WordPress website from the command line by connecting to the server via Secure Shell (SSH). Although WP-CLI works on Windows, it’s designed for UNIX-based environments such as Linux distributions and Mac OS. WP-CLI, or WordPress Command Line Interface, is a tool to set up, configure, and manage WordPress websites using the command line. If you’re a WP Engine or a Flywheel user, you can also clone live sites from your accounts or push local sites to production. Moreover, Local enables you to change your site’s configuration through an easy-to-use dashboard. That means you can have sites that “hibernate” and not consume any resources until you need to use them. Local enables you to create as many local websites as you wish and start or stop them. One of the advantages of using Local is that you don’t have to install WordPress manually. With WampServer, you get an Apache, PHP, and MySQL stack.īy contrast, XAMPP offers an environment that includes Apache, MariaDB, PHP, and Perl: If you’re using Windows, your choice of local development environment installers will be between WampServer and XAMPP. Instead of relying on the command line, you can configure the software stack using a Graphical User Interface (GUI). The advantage of using one of these installers is that, in most cases, it also includes some type of management dashboard. There are software packages designed to help you install all the local server requirements. Use Local Development Environment Software Installers However, there’s no reason to do this when there are several tools to simplify the process. You can install all of those elements manually. That means installing WordPress’s software, including PHP, web server software, and MySQL or MariaDB. To create a local WordPress website, you need to set up a development environment.
#Local by flywheel vs xampp how to#
How to Create a Local WordPress Website (3 Methods) However, some local WordPress development tools enable you to bypass that problem by creating temporary links that give external users access to your local sites. The only practical downside of using a local WordPress site is that users outside of your network won’t be able to access it. That setup enables you to create local staging copies of a live site and use them for testing.
#Local by flywheel vs xampp full#
Thanks to migration and backup plugins, it’s relatively easy to export and import full sites in WordPress. Local websites can also double as staging environments.
#Local by flywheel vs xampp update#
You need to update critical components of your website.You’re developing or testing a theme or a plugin.You’re working on a new website, but you’re not ready to publish it yet.Some of the specific situations where we recommend using local WordPress websites include: If you have a hosting plan that limits the number of websites that you can set up, a local environment lets you create new projects at no additional cost. Traditionally, local WordPress websites are meant for development and testing purposes. Let’s get to it! When to Use a Local WordPress Website In this article, we’ll discuss when it makes sense to use a local WordPress website, and then we’ll show you three ways to create one. However, since you’re using a local environment, the website should instantly load. You can install plugins and themes, access the site’s core files, and edit its code. Local WordPress sites are amazing tools for development and testing, and best of all, they’re free to use.Ī local WordPress website works just like any regular installation. However, you can also create a “local” site that only you and other users within your network can access. In most cases, you want as many people as possible to visit your website.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
